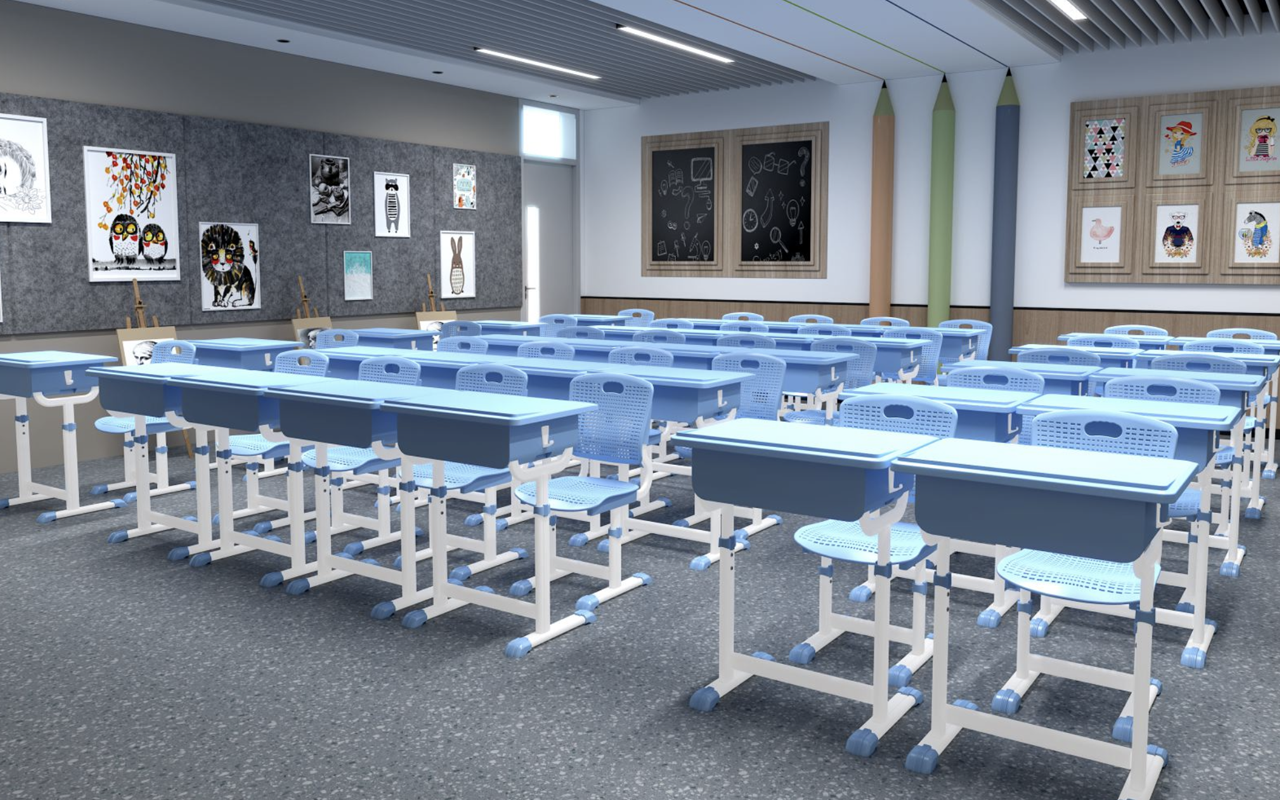
The materials used in student school desks play a pivotal role in ensuring durability, safety, and functionality in educational environments. As classrooms evolve to meet modern pedagogical demands—such as flexibility, sustainability, and ergonomic design—three materials have emerged as leading choices for desktop surfaces: E1 grade MDF, polypropylene (PP), and acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS). This article explores the advantages of each material, providing insights to help educators and designers make informed decisions.
- E1 Grade MDF: The Sustainable and Safe Choice Medium-density fibreboard (MDF) is a composite wood product engineered from wood fibers, resin binders, and wax. The E1 grade designation refers to its low formaldehyde emissions, a critical factor for indoor air quality in schools 210.
Advantages:
Health and Safety: E1 grade MDF emits ≤0.07 ppm formaldehyde, reducing risks of respiratory irritation and long-term health issues linked to traditional MDF 213. This aligns with trends in school construction prioritizing non-toxic materials 6.
Durability: Resistant to warping and cracking, E1 MDF withstands daily wear and tear. Its uniform density ensures a smooth surface ideal for writing, painting, or veneering 110.
Sustainability: Made from recycled wood fibers and eco-friendly resins, E1 MDF supports green building practices. Schools aiming for certifications like GREENGUARD often favor this material 610.
Cost-Effectiveness: While pricier than standard MDF, its longevity reduces replacement costs. Pre-cut panels also simplify installation 210.
Limitations:
Requires sealing to prevent moisture damage.
Heavier than PP or ABS, limiting portability in modular designs 14.
Best For: Classrooms prioritizing safety, sustainability, and traditional aesthetics.
- Polypropylene (PP): Lightweight and Chemical-Resistant Polypropylene, a thermoplastic polymer, is increasingly used in modern school furniture due to its versatility and resilience.
Advantages:
Lightweight and Portable: PP’s low density (0.9 g/cm³) makes desks easy to reconfigure, supporting active learning trends like collaborative “learning hubs” 5712.
Moisture and Chemical Resistance: Impervious to spills and cleaning agents, PP is ideal for science labs or cafeterias. Unlike MDF, it won’t swell or degrade when wet 47.
Cost-Efficient: PP is cheaper than ABS and many wood composites, making it suitable for budget-conscious projects 7.
Eco-Friendly Options: Recyclable and often made with post-industrial waste, PP aligns with schools’ sustainability goals 612.
Limitations:
Lower tensile strength (4,800–5,800 psi) compared to ABS, limiting load-bearing capacity 57.
Prone to warping under prolonged heat exposure.
Best For: High-traffic areas requiring easy mobility and resistance to spills.
- ABS: The Durable and Ergonomic Option ABS, a thermoplastic blend, combines rigidity with impact resistance, making it a premium choice for heavy-use environments.
Advantages:
Strength and Durability: With a tensile strength of 6,100–7,800 psi, ABS outperforms both MDF and PP. It resists dents, scratches, and sagging, even under heavy textbooks or equipment 57.
Heat Resistance: ABS withstands temperatures up to 215°F, reducing deformation risks in sunlit classrooms or near heating systems 7.
Design Flexibility: Easily molded into ergonomic shapes, ABS supports curved edges and integrated features like cable management for tech-friendly desks 712.
Low Maintenance: Non-porous surfaces resist stains and bacteria, ideal for hygiene-focused settings 7.
Limitations:
Higher cost than PP and E1 MDF.
Environmental concerns due to petroleum-based production and limited recyclability 7.
Best For: STEM labs, vocational training spaces, or institutions prioritizing long-term durability.
Post time: Apr-10-2025